Why and How to Use Fine-Tuning with OpenAI Models
Fine-tuning is a powerful tool when a model's default responses don’t meet your specific expectations. It allows you to train a base model on your own dataset, resulting in:
- Higher quality results in specialized tasks.
- Shorter prompts, reducing token usage.
- Lower response latency.
When Is Fine-Tuning the Right Choice?
Fine-tuning makes the most sense when showing the model what to do is easier than describing it in prompts. It is particularly effective when your user needs are:
- Well-defined.
- Repeatable.
- Pattern-based.
Common Use Cases
- Customizing response tone or style.
- Ensuring a consistent output format.
- Handling edge cases more reliably.
- Categorizing data automatically.
Preparing Your Data
To train an OpenAI model, you’ll need to provide a .jsonl (JSON Lines) file. This format stores one JSON object per line. Here's an example:
{"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "Marv is a factual chatbot that is also sarcastic."},
{"role": "user", "content": "What's the capital of France?"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "Paris, as if everyone doesn't know that already."}
]}
Each object contains a conversation with a system message, a user messageand the assistant's response. The more examples you provide, the better the model will generalize.
Real-World Example
Imagine building an app that converts input words (e.g., verbs, nouns) into grammatically correct sentences. You want the model to transform input like "mom, I, yesterday, be, forest" into "Mom, I was in the forest yesterday."
Example Dataset
Mom, I, want, cookie; Mom, I want a cookie.
I, be, yesterday, outside; I was outside yesterday.
Converting Your Dataset to JSONL
Here's a Python script that takes a plain-text file with your input/output pairs and converts it to the correct .jsonl format:
import json
import sys
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
print("Usage: python convert.py <input_file_name>")
sys.exit(1)
input_file = sys.argv[1]
try:
with open(input_file, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
data = f.read()
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"File {input_file} does not exist.")
sys.exit(1)
lines = data.strip().split("\n")
output = []
def process_line(line):
input_part, output_part = line.split("; ")
return {
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "Fix the grammar of the sentence."},
{"role": "user", "content": input_part.strip()},
{"role": "assistant", "content": output_part.strip()}
]
}
for line in lines:
output.append(process_line(line))
output_file = "fine_tuning_grammar.jsonl"
with open(output_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for item in output:
f.write(json.dumps(item, ensure_ascii=False) + "\n")
print(f"Data written to {output_file}")
After running this script, you’ll have a properly formatted training file, ready for upload.
Running the Fine-Tuning Job
Once your .jsonl file is ready:
-
Log in to the OpenAI platform.
-
Go to the Fine-tuning tab in the dashboard.
-
Click Create a fine-tuned model.
-
Choose the base model (e.g., gpt-4-mini for lower cost).
-
Upload your file and follow the validation steps.
Validation will check for formatting errors and any content that violates OpenAI's policies. The fine-tuning process may take several minutes depending on the size of your dataset.
Training Results and Visualization
After training, OpenAI provides a loss chart that shows how the model's accuracy improves over time. A flattening green line typically indicates convergence on the test dataset.
Using Your Fine-Tuned Model via API
Once training is complete, copy the value of the Output model and use it in the API request:
Code Example
import openai
openai.api_key = "your-api-key"
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="your-fine-tuned-model-id",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "Fix the grammar of the sentence."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Mom, I, want, cookie"}
]
)
print(response["choices"][0]["message"]["content"])
Example
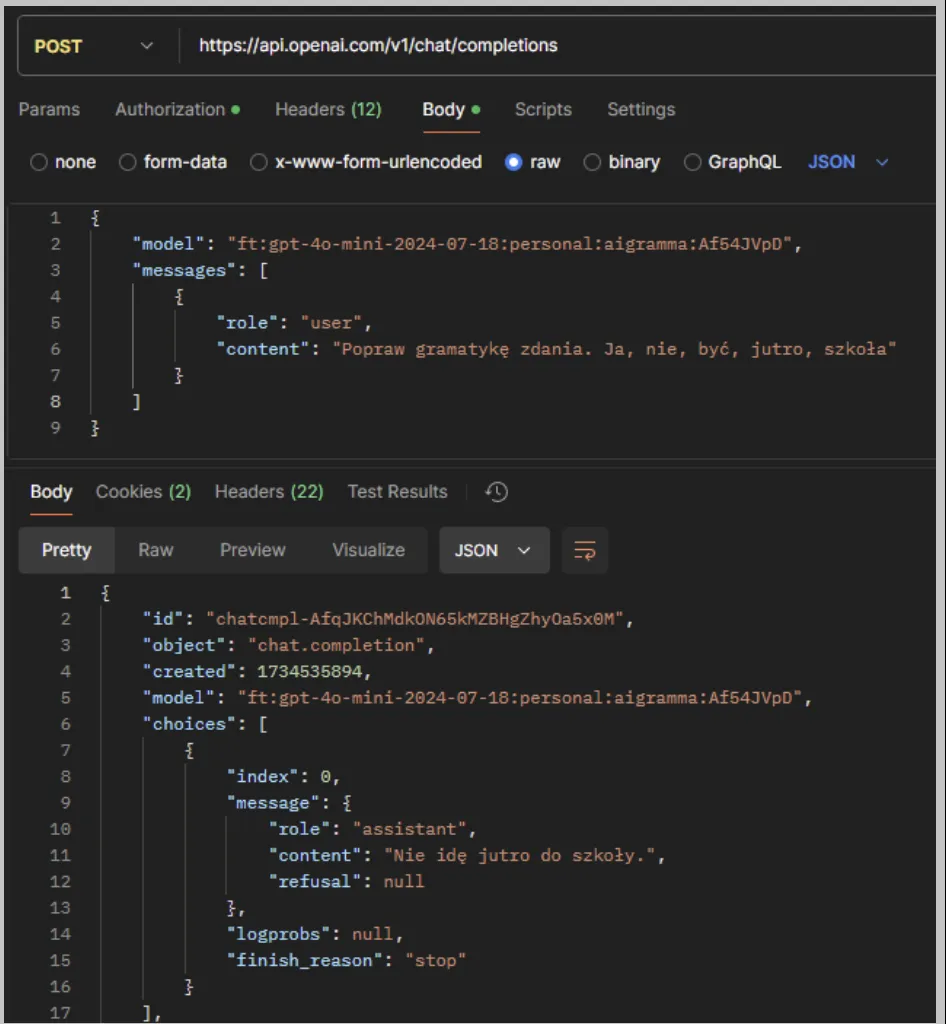
Conclusion
Fine-tuning gives you precision control over how the model responds. With a well-structured dataset and a clear goal, you can dramatically improve the quality, consistencyand relevance of your AI outputs.
