Introduction to LLMs: What Are They and How Do They Work?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are AI algorithms trained on massive amounts of text data. This training enables them to analyze and generate human-like language by recognizing complex patterns and relationships between words. However, models trained on outdated data might struggle to understand recent slang or new terminology.
How Are LLMs Built?
LLMs are based on neural network architectures, typically transformers. These networks consist of three main components: an input layer, multiple hidden layersand an output layer. This layered structure allows LLMs to process information in a non-deterministic way — meaning they can generate different responses to the same prompt.
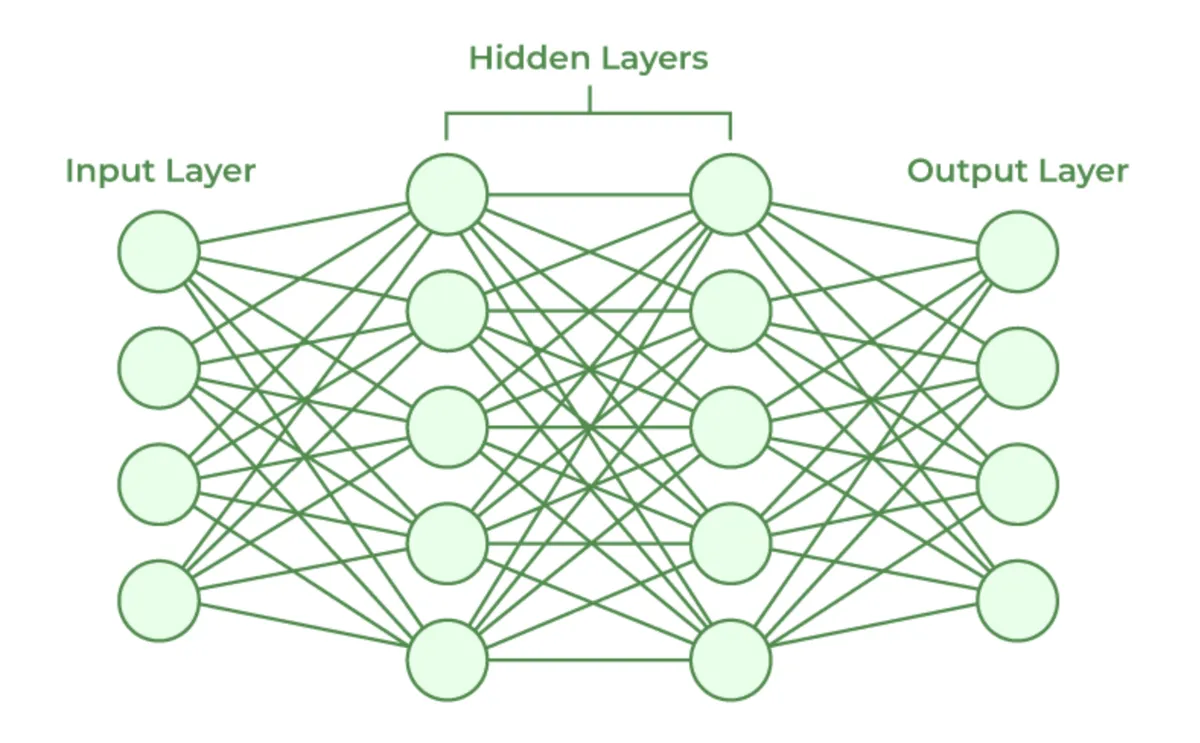
The input layer receives data like text or images. Hidden layers contain neurons that extract features and process the data. The more layers and neurons, the more complex the patterns the model can understand. Finally, the output layer generates a response.
Example: Image Recognition with LLMs
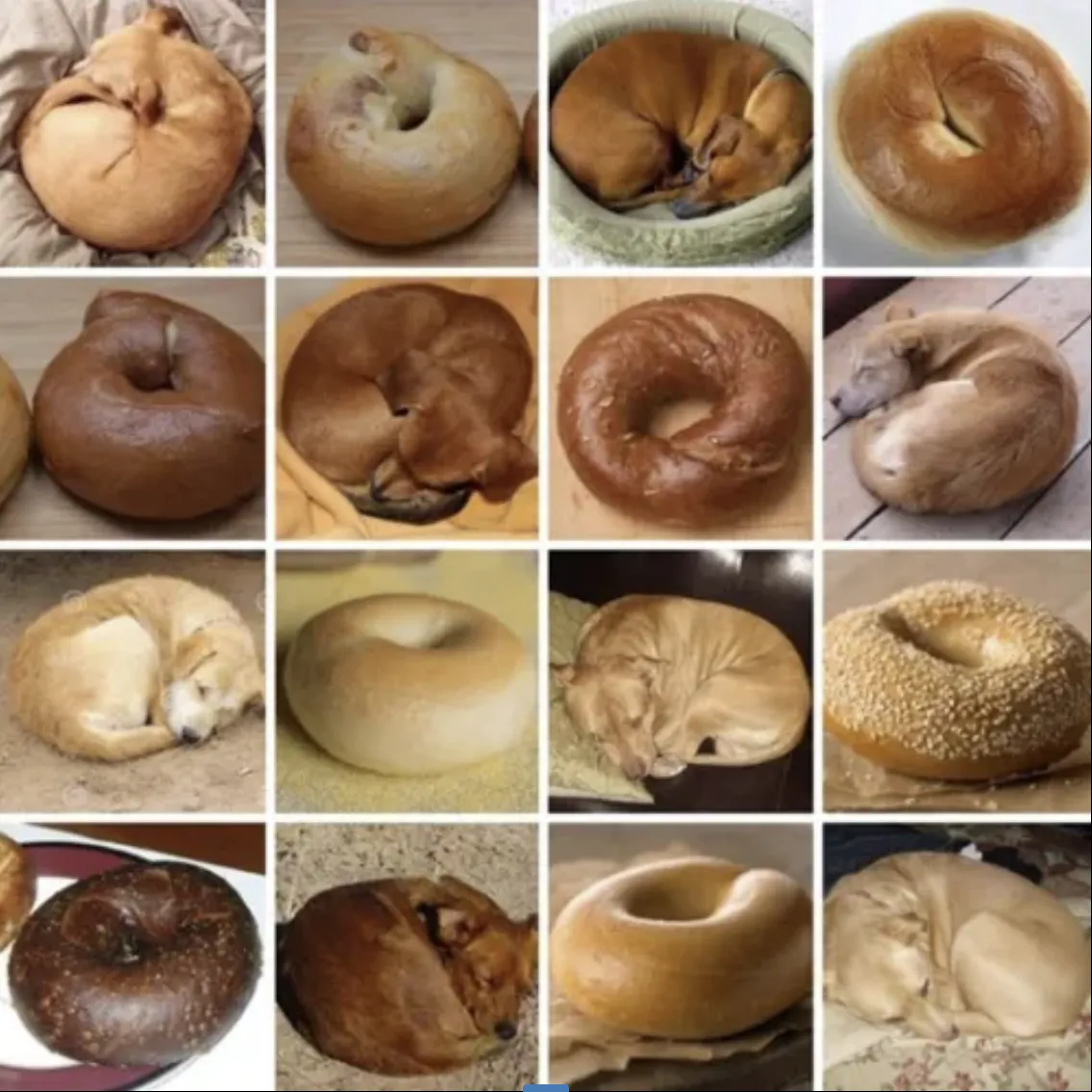

Imagine an LLM designed to recognize sleeping dogs in images. The input layer processes the image, hidden layers analyze shapes, texturesand patternsand the output layer determines the presence of a dog — with a probability score. The process isn't deterministic: the same input might produce slightly different results each time.
What Are Tokens?
In the context of LLMs, a token is a unit of text the model processes. Depending on the model's tokenizer, a token might be a whole word, a single letter, punctuation, or a word fragment.
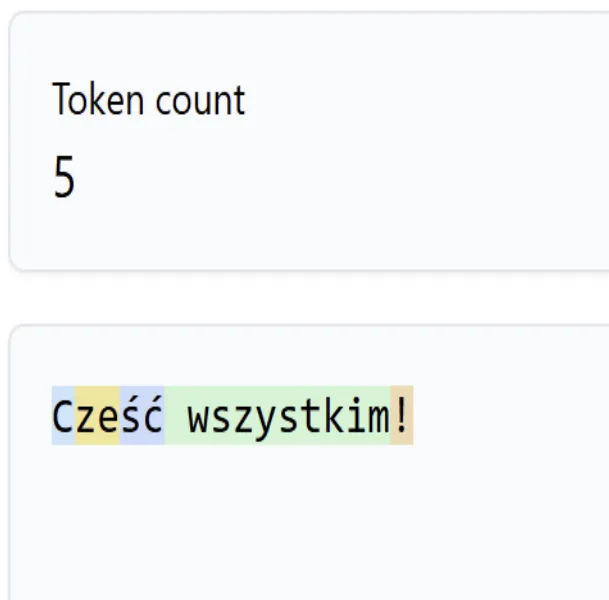
Tools like Tiktokenizer can show how a piece of text is broken into tokens. Each token has a numeric ID that the model uses internally.
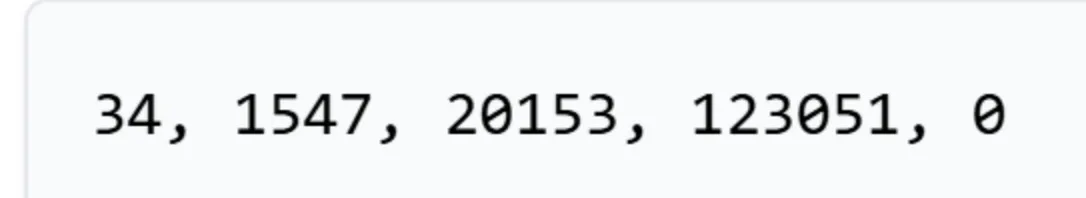
Token count impacts both performance and cost. Longer inputs require more computational power and may exceed the model’s token limit. Efficient token usage is essential for optimal performance.
How Does an LLM Generate a Response?
LLMs generate one token at a time. The process repeats until a complete answer is formed. If you’ve used ChatGPT or Gemini, you’ve likely seen the response appear gradually — that’s token-by-token generation in action.
The model relies on the entire conversation context. It considers not only the user's latest message but also its own previous replies. This helps maintain continuity, but it can also cause the model to loop or repeat itself if it misinterprets the context.
Fine-Tuning vs. RAG
To tailor a model’s behavior or expand its knowledge, two popular techniques are used: Fine-Tuning and RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation).
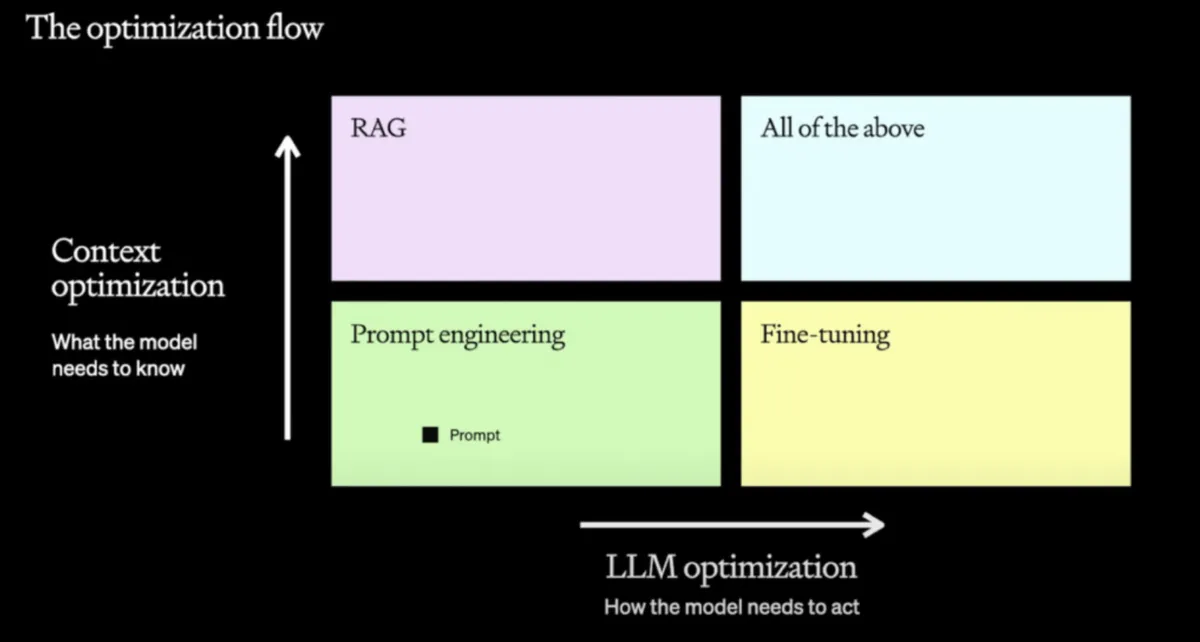
Fine-Tuning
Fine-tuning involves training the model on custom datasets to teach it how to respond in specific ways.
Example: If you want the model to convert support tickets into tasks for different teams, fine-tuning it on a dataset with such examples will help it learn the desired output format.
Benefits:
- Improved quality: Tailored responses for specific needs.
- Efficiency: Generates better answers using fewer tokens.
- Customization: Adapts to internal language and workflows.
Although it can be costly, fine-tuning often results in long-term savings due to faster and more accurate outputs.
RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation)
RAG combines an LLM with external data sources. Since standard models don’t access the internet post-training, RAG provides them with up-to-date information from documents, databases, or APIs.
How It Works: Upload a documentation file or knowledge baseand the model can use it to answer questions. This allows for accurate, context-aware responses beyond the model’s original training.
Use Cases:
- Customer Support: Integrate product documentation so the model answers user questions.
- Internal Tools: Load company processes to assist employees.
- Education: Use custom course material for tutoring purposes.
Advantages of RAG:
- Current knowledge: Keeps model responses relevant without retraining.
- Flexible: Adaptable to different industries.
- Cost-effective: Avoids full-scale fine-tuning for minor updates.
LLMs are powerful tools that transform how we interact with machines. Whether you’re fine-tuning for performance or using RAG for dynamic knowledge injection, understanding how these models work is the first step to leveraging them effectively.