Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 are designed to process natural language in a way that closely mimics human interaction. While this opens up exciting possibilities, it also introduces the need for a structured approach to communication with the model—this is where prompt engineering comes in.
What Is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering is the practice of designing prompts (inputs to the model) with a specific objective in mind. The structure and clarity of a prompt can dramatically influence the quality of the model’s output.
Why English Is the Preferred Language
Although many LLMs support multiple languages, most are optimized for English. As the chart below shows, English prompts outperform Polish by 3.4% in model effectiveness.
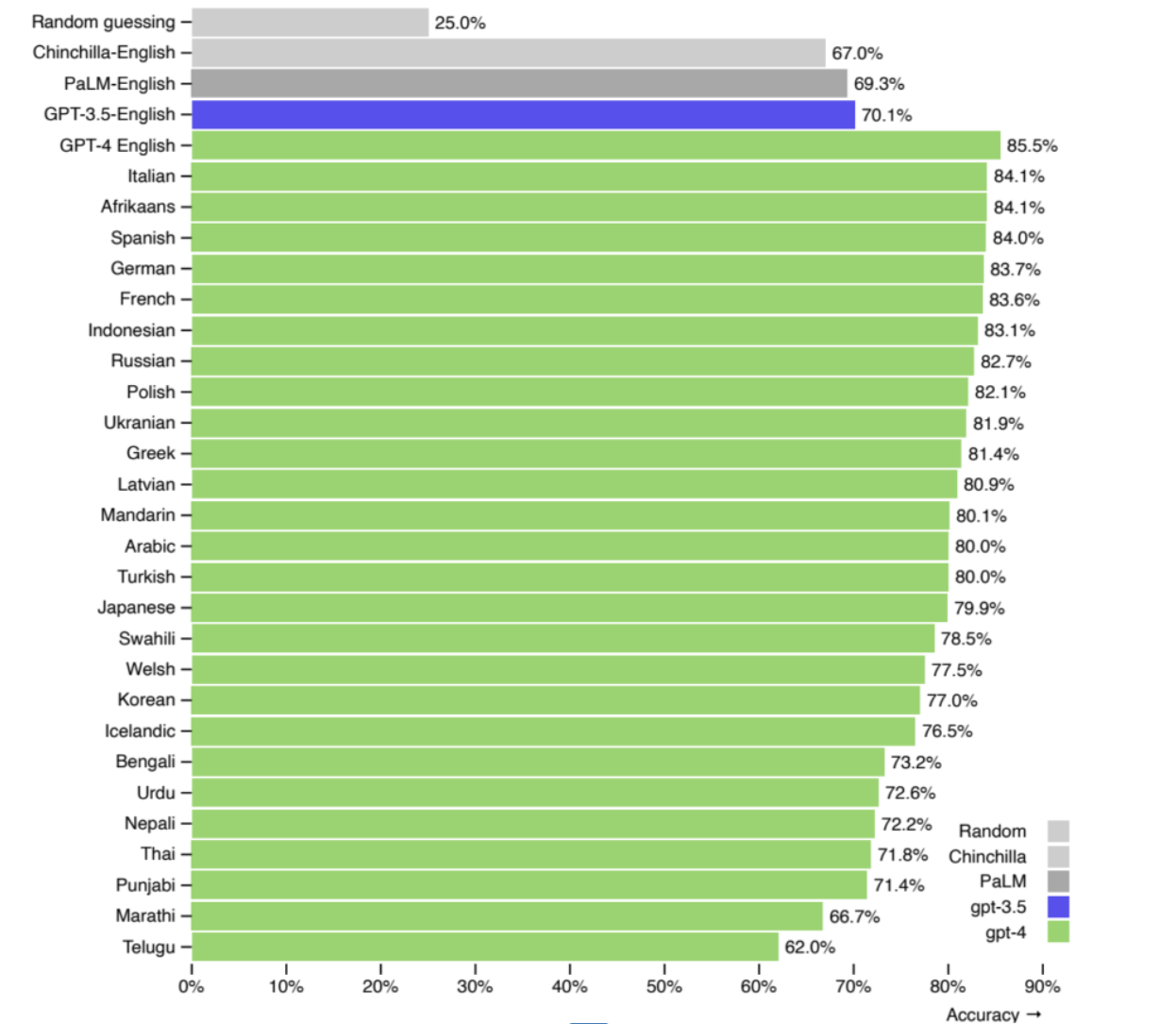 Source: OpenAI
Source: OpenAI
Even a small performance gap can significantly impact production-level applications. That’s why English is recommended for mission-critical use cases, while other languages may be fine for local or experimental purposes.
The Context Window: Mind the Tokens
Each LLM has a context window, which is the maximum number of tokens (words and symbols) it can handle in a single prompt + response cycle.
Why This Matters
If your input and output exceed the token limit, parts of the prompt may be ignored, leading to incomplete or incorrect responses. You can use tools like Tiktokenizer or Microsoft’s Tokenizer library to analyze token counts.
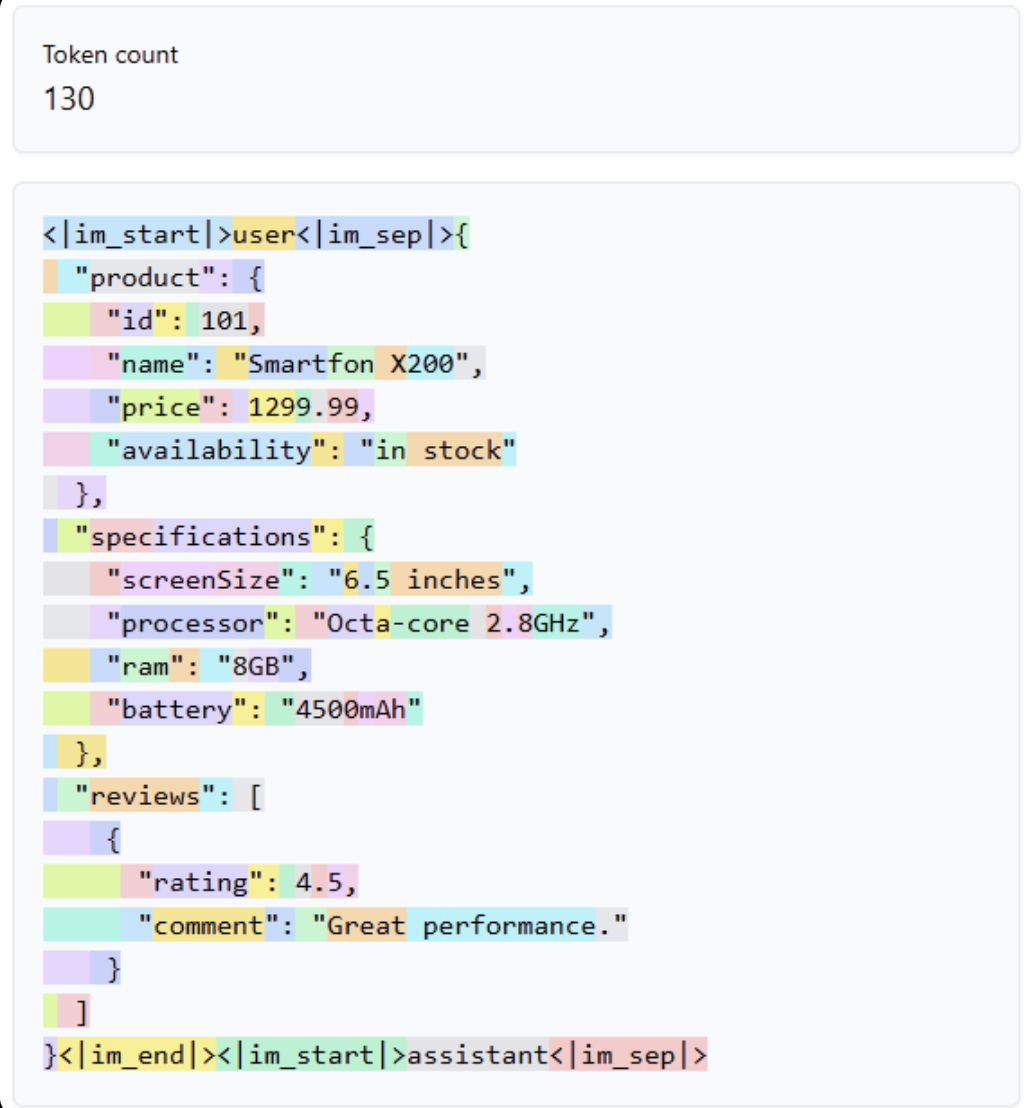
Data Format and Token Count
The structure of your input data affects token usage. Consider the following example JSON:
{
"product": {
"id": 101,
"name": "Smartphone X200",
"price": 1299.99,
"availability": "in stock"
},
"specifications": {
"screenSize": "6.5 inches",
"processor": "Octa-core 2.8GHz",
"ram": "8GB",
"battery": "4500mAh"
},
"reviews": [
{
"rating": 4.5,
"comment": "Great performance."
}
]
}
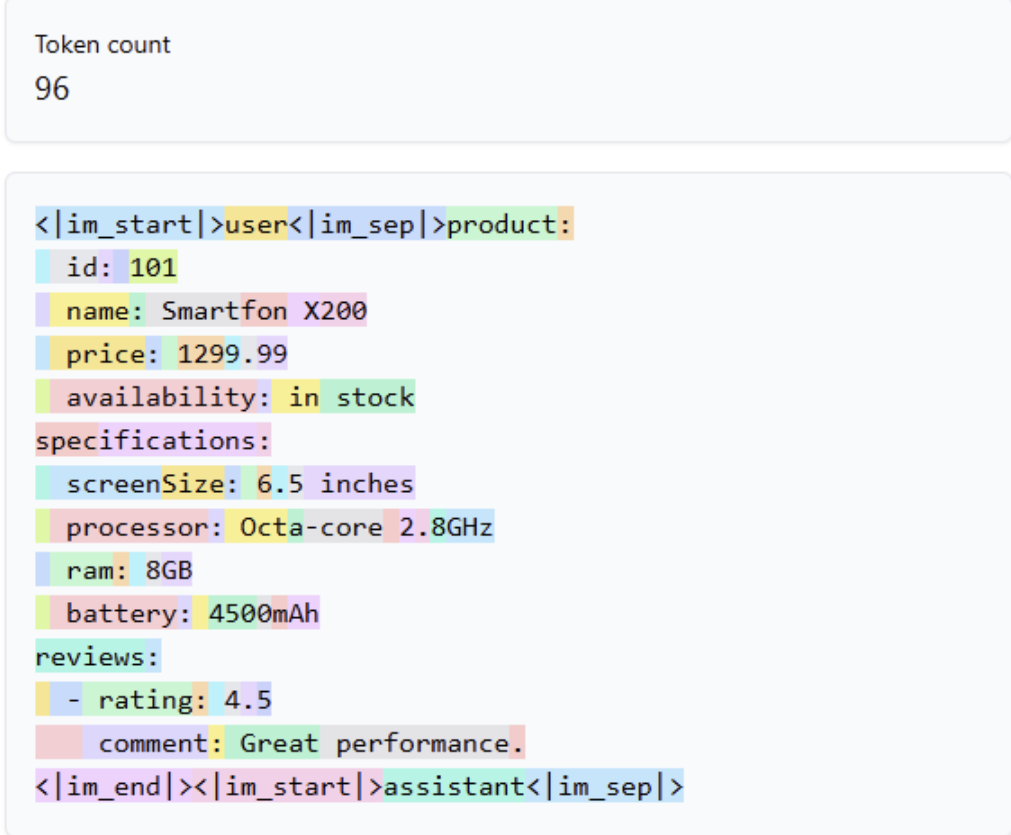
The same data in YAML format uses 34 fewer tokens. That may not seem like much, but across thousands of requests, it adds up.
How to Optimize Your Prompts
1. Restrict Context
Assign the model a specific role and clearly define the problem. Example:
 Source: OpenAI Prompt Examples
Source: OpenAI Prompt Examples
2. Set Clear Objectives
Tell the model what format you expect. For example:
Return the output as a JSON list matching the schema below.
3. Define Rules
Use numbered or bulleted lists to outline constraints, edge casesand expected behaviors. Clearly state how the model should behave under normal and edge-case conditions.
4. Provide Data
If the model needs context (e.g., a document or search results), wrap it in a section and refer to it explicitly:
<user_data>
...user input...
</user_data>
When responding, use only information from <user_data>.
5. Give Examples
LLMs are excellent at pattern recognition. Include positive and negative examples to guide output.
6. Let the Model Think
Use a chain-of-thought approach:
Think step-by-step before giving your final answer.
This often improves accuracy and reasoning.
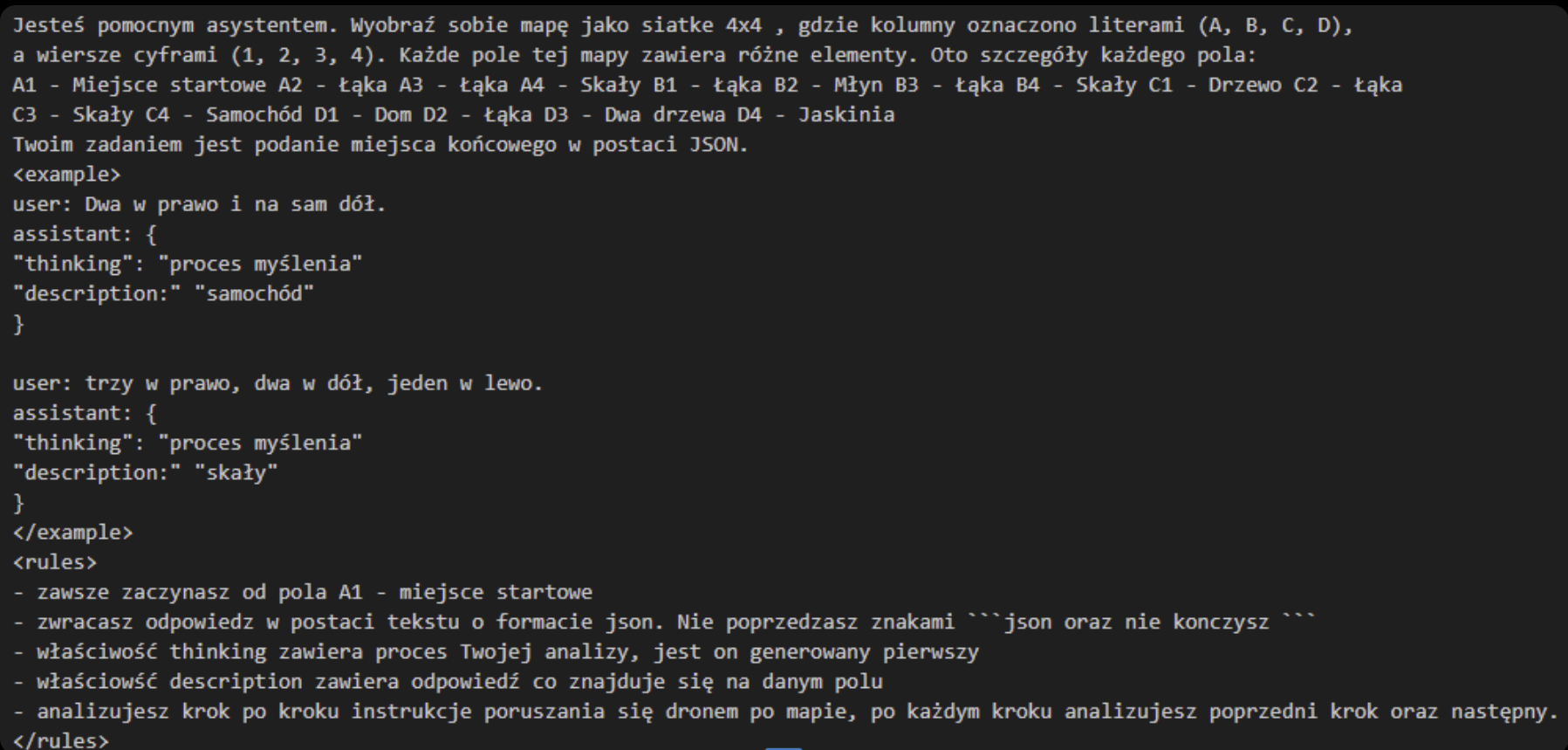
Case Study: Prompt from AI Devs Course
In an AI Devs training, I crafted a prompt instructing the model to parse a JSON-based map and return a description of a field’s contents. The prompt was segmented using XML-like tags for clarity. This structure made it highly maintainable and readable.
Monitoring Prompts
LLMs are non-deterministic—outputs can vary. Since there’s no debugger, tracking and analyzing responses is essential.
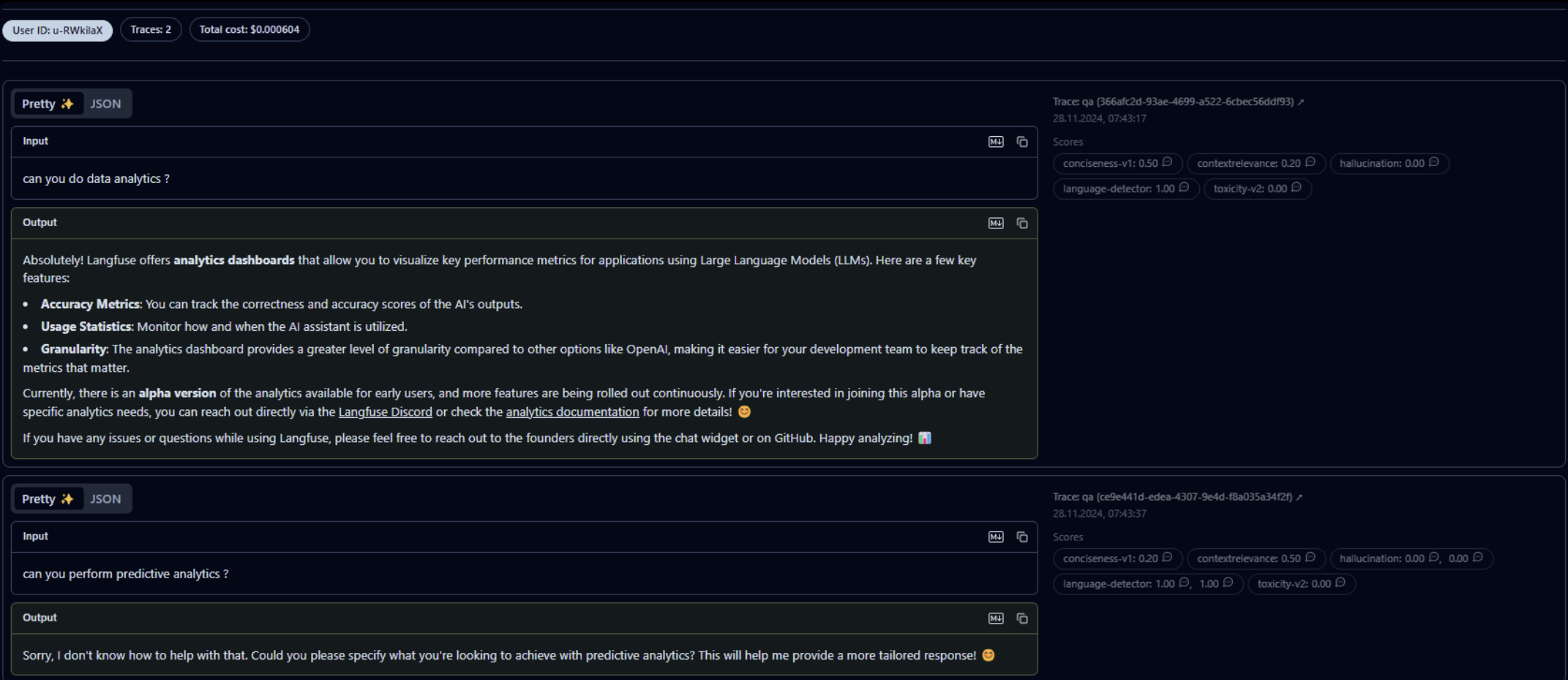
LangFuse
LangFuse is a tool for monitoring LLM behavior. It lets you:
- View conversation history
- Track token usage and costs
- Analyze prompt effectiveness
Highly recommended for anyone building LLM-powered applications.
Example: Why Monitoring Matters
In one case, a prompt worked perfectly unless the user input included a misleading command. The model then followed the user input instead of the system prompt.
Solution: Strengthen the system prompt to override misleading user instructions.
Conclusion
When working with LLMs, writing good prompts is a critical skill—especially in software development. In production environments, prompts are often generated dynamically based on user input, business logicand system state. Mastering prompt engineering helps ensure your AI applications are reliable, accurateand cost-effective.
