What is a Vector Database?
In mathematics, a vector basis refers to a set of vectors that are linearly independent and span the entire vector space. In simpler terms, vector bases are a way to describe a space in the simplest possible way using the minimum number of elements.
Vector Databases in AI Context
When building solutions based on LLM models, especially in the context of data collection and search, we deal with vector databases and vector embeddings. This involves checking the semantic proximity of data points, where input data (e.g., user questions, documents, content) is transformed into vector representations. These allow for efficient comparison and searching of data, even if they don't have identical vocabulary but are semantically similar.
Embeddings
Embedding is the process of creating vectors from data. This process enables the transfer of semantic meaning into numbers. You regularly encounter such mechanisms when using recommendation engines, voice assistants, or language translators.
A paragraph, text, single word, etc. can be encoded as a vector. For this purpose, an Embedding Model is necessary, which is responsible for converting data into vectors.
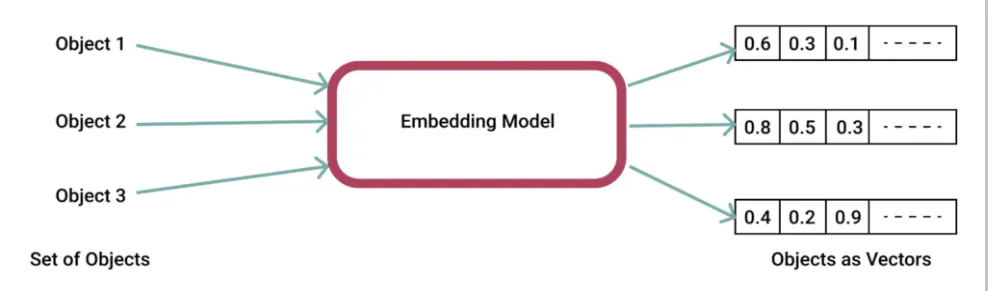 Source: pinecone.io
Source: pinecone.io
Applications of Vector Databases
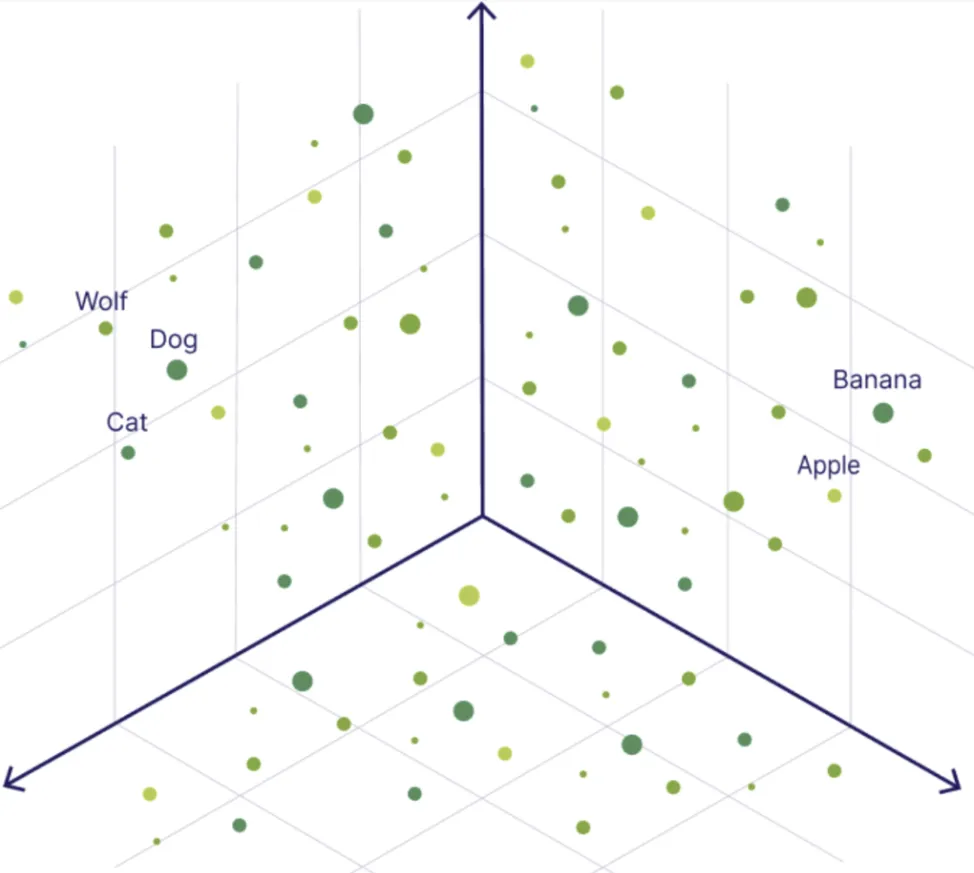
Let's imagine a set of data stored in a vector database. Let's visualize them in a three-dimensional space (in reality, vectors can be from nearly 100 to 4000 dimensions).
 Source: weaviate.io
Source: weaviate.io
We can see that dog, catand wolf are positioned close to each other. Wolves and dogs are placed close together because dogs are close descendants of wolves. Similarly, cats and dogs are fairly classic pets.
On the other side, we have apple and banana. These are fruits, so they lie close to each other and on the opposite side, as they are not associated with animals in any way.
This example shows how a vector database works. At this point, if a user started searching for the word banana, there's a high probability they would also receive information about apples.
Summary
Vector Embedding is a numerical representation of data of various types, such as text data, images, or sounds. They can capture semantic relationships between data objects, allowing for finding similar data points by identifying their nearest neighbors in high-dimensional vector space.